Cyber Security

Cyber security stands as one of the fastest-growing and most dynamic fields in technology today. As cyber threats continue to evolve, the demand for skilled professionals to protect digital assets has never been greater. For newcomers, the vast array of roles and responsibilities within cybersecurity can feel overwhelming. Likewise, recruiters may face challenges in identifying the right talent for specific roles.
This guide simplifies the path into cybersecurity by breaking down its diverse domains, helping aspiring professionals explore career options, and enabling recruiters to make informed hiring decisions.
Why Choose Cyber security?
As businesses embrace digitization, they gain convenience but also expose themselves to potential vulnerabilities. Cyber security professionals are at the forefront of safeguarding sensitive information, ensuring compliance, and preserving trust in digital systems.
The field is not only vital but also rewarding, with a global workforce gap of over 3.4 million professionals. For motivated individuals, cyber security offers unparalleled opportunities to make an impact, grow professionally, and earn competitive compensation.
Exploring the key Cyber Security Domains
Cyber security is not a single career path but an umbrella encompassing diverse roles, each requiring unique skill sets and expertise. Below is an overview of the major domains to help you navigate this exciting field:
- 1. Network Security
- Focuses on protecting the integrity of a network and its data. Professionals in this domain implement firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and VPNs to prevent unauthorized access.
- 2. Endpoint Security
- Addresses threats to devices such as laptops, smartphones, and servers. Endpoint security specialists work with antivirus solutions, endpoint detection, and data loss prevention tools.
- 3. Identity and Access Management (IAM)
- Centers on ensuring the right individuals access the right resources at the right time. IAM experts design authentication methods, implement single sign-on (SSO), and manage privileged accounts.
- 4. Infrastructure Security
- Involves securing physical and virtual infrastructure, including servers, storage, and cloud environments. Professionals in this domain protect critical systems against attacks and unauthorized changes.
- 5. Governance, Risk, and Compliance (GRC)
- Focuses on aligning cyber security strategies with business goals, managing risks, and ensuring adherence to regulatory standards. GRC experts help organizations stay compliant while mitigating risks effectively.
- 6. Data Protection and Privacy
- Deals with securing sensitive information and ensuring compliance with privacy regulations like GDPR and CCPA. Data protection specialists manage encryption, anonymization, and secure data storage.
- 7. Incident Response and Threat Hunting
- Involves detecting, analyzing, and mitigating cyber incidents. Professionals in this area act quickly to contain breaches and investigate potential threats to prevent future attacks.
- 8. Application Security
- Focuses on identifying and fixing vulnerabilities in software applications. Application security professionals conduct penetration testing, secure coding reviews, and dynamic application scanning.
- 9. Emerging Technologies and Trends
- Explores the intersection of cybersecurity with AI, IoT, blockchain, and quantum computing. Specialists in this domain tackle new challenges brought about by innovative technologies.
- 10. Cybersecurity Leadership and Strategy
- Involves senior roles like CISOs who define organizational security strategies, oversee teams, and manage budgets to protect against evolving threats.
Tips for New Talent Entering Cybersecurity
- Identify Your Interests: Explore domains that align with your passion and skill set.
- Build a Strong Foundation: Learn the basics of networking, operating systems, and security principles.
- Earn Certifications: Start with beginner-friendly credentials like CompTIA Security+ or Certified Ethical Hacker (CEH).
- Stay Updated: Follow cyber security trends and keep up with emerging threats to remain competitive.
Making the Match: Tips for Recruiters
- Understand the Domains: Recruiters should familiarize themselves with cyber security specializations to match candidates effectively with roles.
- Evaluate Skills: Assess both technical skills and soft skills, such as problem-solving and communication.
- Look for Certifications: Credentials like CISSP, CEH, and CompTIA Security+ indicate expertise in specific areas.
- Promote Growth Opportunities: Highlight opportunities for professional development and up-skilling in job postings.
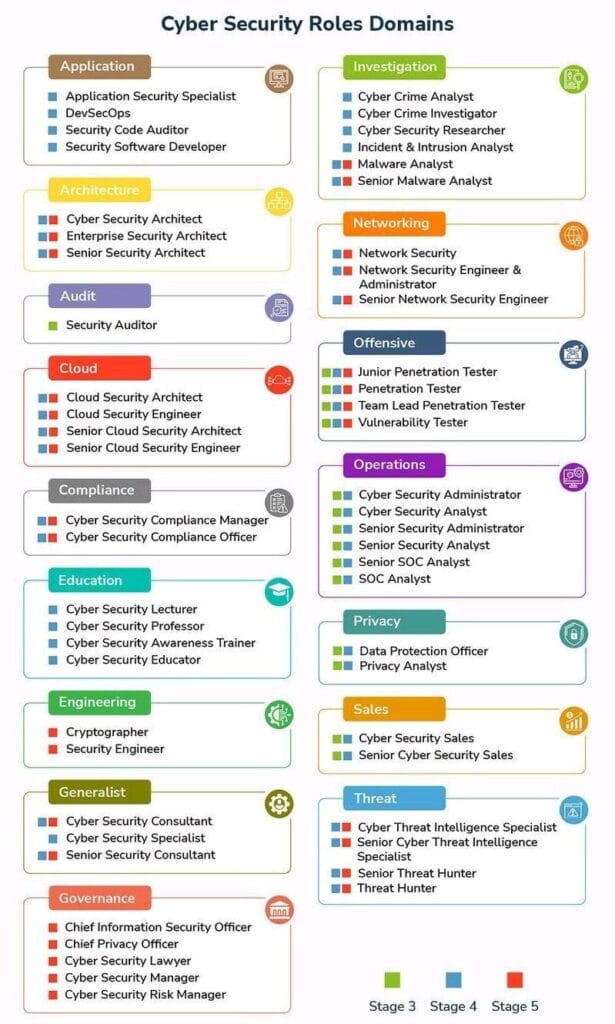
Cybersecurity Domains at a Glance
Conclusion
Cybersecurity offers a rich and rewarding career landscape for those willing to explore it. Whether you’re a newcomer looking to make your mark or a recruiter seeking top talent, understanding the domains within cybersecurity is the first step. By aligning skills, interests, and opportunities, we can build a stronger, more resilient digital future.


