Introduction
The Unified Payments Interface (UPI) has revolutionized digital transactions in India, offering a fast, seamless, and secure payment method for millions of users. With over 10 billion transactions recorded monthly, UPI has become the backbone of India’s cashless economy. However, as its popularity has surged, so too have the instances of UPI frauds in India, targeting unsuspecting users. Cybercriminals have adapted their tactics to exploit vulnerabilities in this system through phishing scams, fake payment apps, and fraudulent QR codes. This blog explores how these UPI frauds work, real-world cases, and how users can protect themselves from falling victim to these malicious schemes..
What is UPI?
Unified Payments Interface (UPI) is a real-time payment system developed by the National Payments Corporation of India (NPCI). It enables users to link multiple bank accounts into a single mobile application, facilitating seamless fund transfers without the need to share sensitive bank information. UPI transactions are authenticated using two-factor authentication (2FA) and secured with encryption, making it a preferred payment method across India.
How Cyber criminals Exploit India’s UPI for Money Laundering Fraud
Exploitation Techniques
Cyber criminals use many tactics to exploit vulnerabilities in the UPI system, and they capitalize on the weaknesses in these authentication mechanisms, unsuspecting users, and loopholes in transaction protocols.
• Phishing attacks are those where malicious actors impersonate legitimate entities and trick unsuspecting users into giving out sensitive information like their login credentials and OTPs (One-Time Passwords). They use this to gain unauthorized access to UPI accounts.

Malware infiltration
techniques like distributing malicious software through infectious attachments and links enable these cybercriminals to compromise unsuspecting users’ devices and manipulate transactions without their knowledge.
Laundering Mechanisms
Cybercriminals employ sophisticated laundering techniques as they gain access to compromised UPI accounts. It involves using a multi-layered process of funnelling stolen funds using a complex network of shell companies, intermediary accounts, and cryptocurrency exchanges to hide the trail. Cybercriminals launder massive sums of money by leveraging the anonymity provided by cryptocurrency and offshore banking options. They launder and evade detection by law enforcement authorities.
Impact on Financial Integrity
UPI money laundering fraud presents a massive risk to India’s financial integrity. It undermines the public’s trust in digital payment platforms and erodes investor confidence. Additionally, it tarnishes India’s reputation in the FinTech sector and stifles its growth potential. Investors and consumers become wary of participating in a system affected by security vulnerabilities and fraudulent activities. Money laundering fraud and its prevalence present many other societal risks as the potential for funding illicit activities like organized crime, drug trafficking, and terrorism. These can have far-reaching results for national stability and security.
Regulatory Challenges
Digital payment ecosystems are going through a rapid evolution and have outpaced regulatory frameworks and oversight mechanisms. It leaves significant gaps that cybercriminals exploit to perpetrate illicit activities with impunity. Regulatory agencies still struggle with the evolving nature of cyber threats, even though efforts to improve cybersecurity regulations and strengthen KYC norms are ongoing. Moreover, they grapple with the complexities of enforcing compliance across a diverse and vast landscape. In addition, the cross-border nature of these schemes presents jurisdictional issues, which, in turn, hinder effective coordination and enforcement among international law enforcement agencies. Consequently, addressing these challenges requires enhanced global cooperation and continuous adaptation of cybersecurity measures.
Mitigation Strategies
Stakeholders should adopt a multi-faceted approach encompassing improved KYC protocols, cybersecurity measures, proactive collaboration between law enforcement agencies, financial institutions, and regulators, and real-time transaction monitoring to protect themselves from cyber fraud. It is essential to implement advanced fraud detection algorithms, strengthen authentication systems, and enhance user awareness through training programs, and education are crucial in fortifying the integrity and security of the UPI ecosystem. Furthermore, fostering international information-sharing and cooperation can significantly aid in the disruption and identification of transnational money laundering networks. As a result, this collaboration can help mitigate the global impact of cybercrime on economies and financial systems. In the long run, such efforts will strengthen international financial security and promote more resilient digital ecosystems.
Deep Dive into UPI Frauds: Tactics and Real-World Cases
1. Phishing Scams: Digital Bait for Sensitive Information
Phishing attacks are the most common method cybercriminals use to target UPI users. Fraudsters craft deceptive emails, SMS, or social media messages impersonating banks or payment apps. These messages often contain links to fake websites designed to mimic legitimate portals, prompting users to enter sensitive information like UPI PINs, bank account details, or OTPs.
How It Works:
- Fraudsters send a message claiming issues with your UPI account or offering rewards.
- A fake link redirects to a website mimicking the official UPI app.
- Once users enter their credentials, attackers gain access to their accounts.
Case Study: In 2022, Mumbai police busted a phishing ring that sent SMS messages about fake cashback offers. Victims unknowingly entered their UPI details into a fake site, leading to losses ranging from INR 5,000 to INR 50,000
2. Fake Payment Apps: Disguised Theft
Fraudsters design counterfeit versions of popular UPI apps like Google Pay, PhonePe, or Paytm. While these apps mimic the original UI, they are programmed to capture user credentials and silently transfer funds to the attacker’s account.
How It Works:
- Users download the fake app from unauthorized sources.
- The app requests UPI PIN, promising authentication or a transaction.
- Credentials are then used for unauthorized withdrawals.
Case Study: A Bengaluru-based IT professional lost INR 1.5 lakh by downloading a counterfeit PhonePe app. Although it looked authentic, the app transferred funds directly to the scammer after the user entered their PIN.
3. Fraudulent QR Codes: A Simple Scan, A Big Loss
QR code fraud involves replacing legitimate QR codes with malicious ones, tricking users into sending money to attackers instead of the intended merchant.
How It Works:
- Scammers distribute fraudulent QR codes via email, WhatsApp, or by physically pasting them over genuine QR codes at shops.
- Users scan the code and unknowingly transfer funds to the attacker.
Case Study: In Pune, fraudsters replaced QR codes at popular cafés and grocery stores. Unsuspecting customers lost amounts ranging from INR 500 to INR 5,000.
4. . Remote Access Scams: Hacking via Assistance
Cybercriminals impersonate bank officials or tech support agents, convincing users to download remote access tools such as AnyDesk or TeamViewer.
How It Works:
- The attacker poses as a legitimate agent offering technical support.
- The victim installs remote access software, unknowingly granting control.
- Attackers navigate to UPI apps and transfer funds silently.
Case Study: A Delhi businessman lost INR 2 lakh when a fraudster, posing as a bank officer, gained control of his phone and emptied his UPI-linked bank accounts.
5. SIM Swap Fraud: Gaining Control of Your Number
In this fraud, attackers bypass OTP verification by convincing telecom providers to issue a new SIM card for the victim’s number.
How It Works:
- Fraudsters collect personal information through phishing or social engineering.
- They request a SIM swap from the telecom provider.
- Once successful, they intercept OTPs and execute unauthorized UPI transactions.
Case Study: Hyderabad cybercriminals used SIM swap attacks to steal over INR 5 lakh from unsuspecting victims by exploiting their UPI-linked accounts.
How do hackers execute UPI fraud?
Here’s how hackers execute UPI fraud:
- It starts with a random call from a fraudster who pretends to be a bank representative to get the target’s attention.
- The fraudster asks verification questions like the target’s name, date of birth, or mobile number to make the call sound legitimate.
- The fraudster claims that there is a problem with the UPI app or website and uses technical difficulties to talk to the victim. They create false stories and convince the victim to share their personal information to resolve the issue.
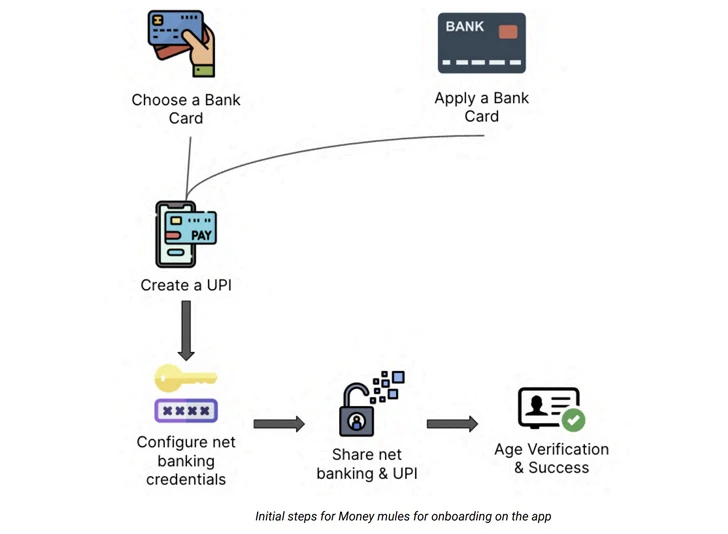
- The fraudster then persuades the victim to download a remote access application, such as AnyDesk or Screen Share, which are readily available on the Google Play Store or App Store.
- During the installation process, the app requests various privacy permissions, similar to any regular application. However, once granted, these permissions allow the fraudster to access nearly everything on the victim’s phone, including sensitive financial information and personal data.
- The fraudster will then ask the victim for the OTP generated on their phone. As soon as the victim reveals the code, the hacker will also ask for permission from the phone.
- When the app acquires all permissions required, the caller starts to take complete control of the victim’s phone without their knowledge. After gaining full access to the phone, the hacker steals passwords and begins transacting with the victim’s UPI account.
Advanced Preventive Measures Against UPI Frauds
- Verify URLs and Links: Always verify a website’s URL before entering sensitive details. Genuine banking URLs use HTTPS with a secure padlock icon.
- Download Only from Authorized Stores: Only use the Google Play Store or Apple App Store to download UPI apps.
- Check QR Codes: Verify QR codes manually with shopkeepers or merchants before scanning.
- Use Strong Device Security: Enable biometric locks, keep antivirus software updated, and use app locks for additional protection.
- Regular Account Monitoring: Check bank statements regularly to detect unauthorized transactions early.
- SIM Swap Detection: Register for alerts that notify you of SIM changes.
- Transaction Limits: Set daily transaction limits to minimize losses in case of unauthorized access.
Tips for Secure UPI Transactions


- 1. Never Share Your UPI PIN: The UPI PIN is like an ATM PIN and should never be shared with anyone, not even with bank officials.
- 2. Beware of Phishing Attempts: You should always remember to not click on links or download attachments from unknown sources. If you cannot avoid them, try verifying the authenticity of those messages and emails.
- 3. Secure Your Mobile Device: We guess you already know that you should use strong passwords and biometric authentication to secure your phone. Try keeping your operating system and apps up to date to protect against vulnerabilities.
- 4. Verify Before Scanning QR Codes: Only scan QR codes from trusted sources. Double-check the recipient’s details before confirming any transaction.
- 5. Monitor Account Activity: Check your bank statements and UPI transaction history, now and then, for any unauthorized activities.
- 6. Educate Yourself and Others: Stay informed about the latest fraud trends and educate family and friends about secure UPI practices.
- By following these UPI fraud prevention tips, users can reduce the risk of falling victim to digital payment frauds.
Government and Regulatory Measures to Combat UPI Frauds
The Indian government and regulatory bodies have implemented several measures to enhance the security of UPI transactions and combat fraud. These measures include:
- To combat UPI fraud, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has issued comprehensive guidelines for banks and payment service providers, aiming to strengthen security protocols and enforce regular audits.
- In parallel, the National Payments Corporation of India (NPCI) and banks run extensive awareness campaigns designed to educate users about safe UPI practices and the dangers of fraud.
- Additionally, mandatory two-factor authentication for UPI transactions provides an extra layer of security for users.

These measures reflect a coordinated effort to protect users and build a secure digital payment ecosystem.
Conclusion
UPI has transformed the financial landscape in India by offering exceptional convenience and accessibility. However, with the rise in digital payments, the threat of UPI frauds has become a pressing concern. By understanding common fraud types, users can reduce the risk of fraud. Preventing digital payment frauds requires collective vigilance and proactive measures from individuals, financial institutions, and regulatory bodies.
By staying informed and cautious, we can enjoy the benefits of UPI while protecting against online payment frauds. Let’s work together to ensure a safe and secure digital payment environment.






